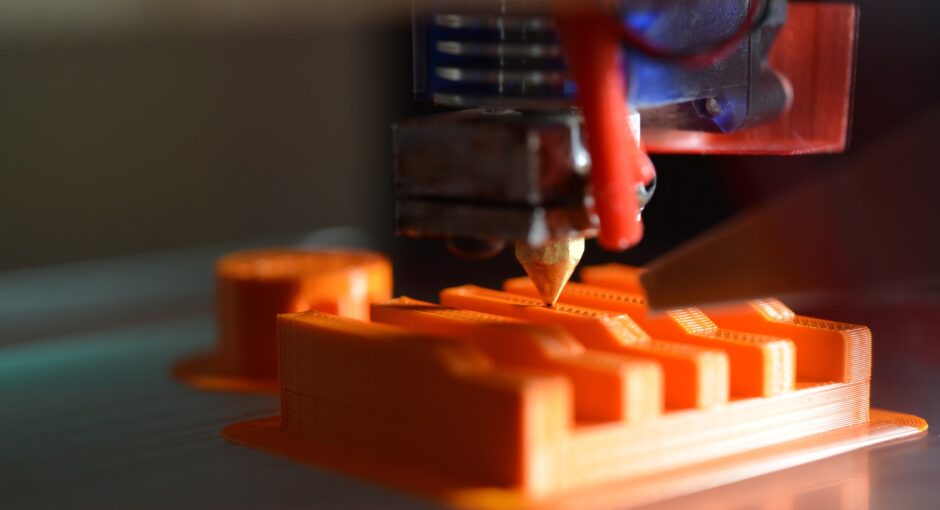
The use of 3D printing technology has allowed for the production of complex parts with intricate geometries and tight tolerances. However, the accuracy of a 3D print is ultimately dependent on the material chosen for the print. Different materials have different properties which can affect the print’s tolerance and dimensional accuracy. Additionally, the material’s mechanical properties can also influence the overall print quality. This article will discuss the impact of material choices on 3D printing tolerances.
Advantages of Different Materials
When choosing a material for 3D printing, it is important to consider the advantages that different materials offer. For instance, metals such as aluminum, titanium, and stainless steel are often used for 3D printing because of their strength and durability. Additionally, these materials are able to withstand higher temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for applications that require high wear and tear. On the other hand, plastics such as ABS and PLA are popular for 3D printing because of their low cost and ease of use. Furthermore, these materials are often used for prototyping and are able to produce accurate and detailed prints.
Factors Affecting Tolerances
The accuracy of a 3D print is dependent on several factors, including the properties of the material used for the print. For instance, the layer height of the print can affect the accuracy of the print, as the smaller the layer height, the more accurate the print will be. Additionally, the temperature used for the print can also affect the accuracy of the print, as higher temperatures can lead to warping and distortion.
The type of 3D printing technology used can also have an effect on the accuracy of the print. For example, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a process that uses a filament of plastic to create a 3D print. FDM prints tend to have lower tolerances than other 3D printing technologies, such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which uses a laser to fuse together powder to create a 3D part.
Impact of Material Properties on Tolerances
The properties of the material used for a 3D print can also have an impact on the accuracy of the print. For instance, the hardness of a material can affect the accuracy of the print, as harder materials tend to produce more accurate prints than softer materials. Additionally, the thermal conductivity of a material can also affect the accuracy of the print, as materials with higher thermal conductivity tend to produce more accurate prints.
The shrinkage rate of a material can also affect the accuracy of the print. Materials with higher shrinkage rates tend to produce more accurate prints than materials with lower shrinkage rates. Additionally, the surface quality of the material can also affect the accuracy of the print, as smoother surfaces tend to produce more accurate prints than rougher surfaces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of material for a 3D print can have a significant impact on the accuracy and tolerance of the print. Different materials have different properties which can affect the accuracy of the print, including the layer height, temperature, and type of 3D printing technology used. Additionally, the properties of the material, such as hardness, thermal conductivity, shrinkage rate, and surface quality, can also affect the accuracy of the print. When selecting a material for a 3D print, it is important to consider these factors in order to ensure a high-quality and accurate print.