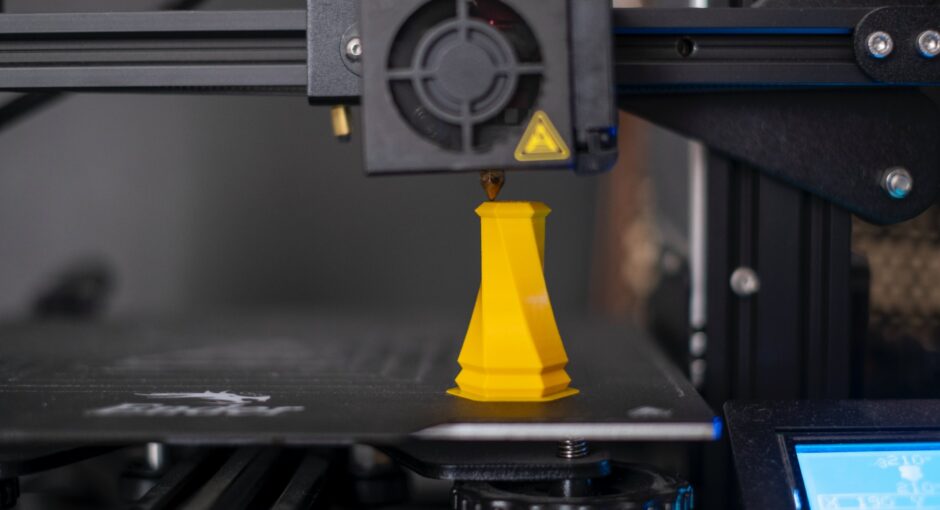
The 3D printing industry has come a long way in recent years. From its humble beginnings as a tool for prototyping and manufacturing, 3D printing has evolved into an advanced technology capable of producing a variety of objects from diverse materials. One of the most exciting developments in the 3D printing space is the emergence of synthetic materials, which offer a range of properties that can be tailored to a variety of applications.
What are Synthetic Materials?
Synthetic materials are those that are produced in a laboratory or factory rather than being sourced from nature. They are typically derived from petroleum or chemical byproducts, making them both cost-effective and durable. Synthetic materials are often used in a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical.
Benefits of Synthetic Materials in 3D Printing
When it comes to 3D printing, synthetic materials offer a range of benefits. One of the most important benefits is cost-effectiveness. Synthetic materials are typically cheaper than naturally-sourced materials, making them ideal for applications that require large volumes of material. Additionally, synthetic materials tend to be stronger and more durable than their natural counterparts, making them suitable for a variety of purposes, from prototyping to final production.
Another benefit of using synthetic materials in 3D printing is the range of options available. Synthetic materials can be customized to meet the specific needs of a project, allowing for the production of objects with unique characteristics. Additionally, synthetic materials can be used in a variety of printing processes, from Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) to Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), making them a versatile option for a range of applications.
Examples of Synthetic Materials in 3D Printing
One of the most popular synthetic materials used in 3D printing is polylactic acid (PLA). PLA is a biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, sugarcane, and cassava. It is a popular choice for 3D printing due to its low cost and ease of use. PLA is also extremely versatile, allowing for the production of objects with a variety of characteristics.
Another popular synthetic material is acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). ABS is a thermoplastic derived from petroleum that is often used in the automotive and electronics industries. It is a popular choice for 3D printing due to its high strength and durability, making it ideal for applications that require objects that can withstand high temperatures and impacts.
Conclusion
Synthetic materials have revolutionized the 3D printing industry, offering a range of benefits that make them ideal for a variety of applications. They are typically cheaper than naturally-sourced materials, making them cost-effective for large-scale projects. Additionally, synthetic materials can be customized to meet the specific needs of a project, allowing for the production of objects with unique characteristics. From PLA to ABS, synthetic materials can be used in a variety of 3D printing processes, making them a versatile option for a range of applications.